Covid-19 Special NRS Pay Point of Sale Pricing: $699 (REG. $1299)
Covid-19 Special NRS Pay Point of Sale Pricing: $699 (REG. $1299)
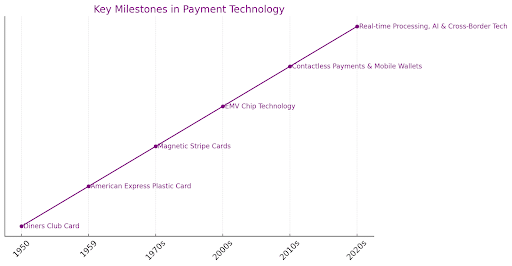
The evolution of credit card processing technology has been marked by significant milestones, transitioning from manual methods to advanced digital systems.
It all began with the introduction of the Diners Club Card in 1950, representing the first multi-purpose charge card. This innovation laid the foundation for developing more universal credit payment systems.
The transition to plastic cards, initiated by American Express in 1959, further revolutionized the industry, creating the credit card imprinter, a significant improvement over manual handwriting.
IBM’s introduction of the magnetic stripe in the 1970s was a pivotal development in credit card processing, allowing for the storage of vital cardholder information and the advent of the first electronic payment terminals.
This shift to electronic processing greatly enhanced the efficiency and security of transactions. In recent years, contactless payment technology has become increasingly prominent, offering a quick and secure transaction method through NFC technology.
EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) technology significantly advances credit card security.
Developed as a joint effort by Europay, Mastercard, and Visa, EMV cards are equipped with a microprocessor chip that enhances transaction security.
This chip technology is a substantial leap from the traditional magnetic stripe, offering a more sophisticated data storage and encryption method.
The primary advantage of EMV technology lies in its ability to reduce fraud, particularly in card-present transactions (where the card is physically used at a point of sale).
Unlike magnetic stripe cards, which store static data, EMV chips create a unique transaction code for each operation, making it significantly more difficult for fraudsters to replicate or clone card information.
This dynamic data authentication ensures that even if transaction data is intercepted, it cannot be reused for fraud.
EMV technology also enhances the overall payment security ecosystem. It supports advanced authentication methods, such as PIN entry and biometric verification, providing an additional layer of security.
The global adoption of EMV technology has led to a noticeable decline in counterfeit card fraud, safeguarding consumers and merchants in their transactional activities.
Encryption is crucial in securing credit card data during transmission, ensuring the confidentiality and integrity of sensitive financial information.
Whenever a credit card transaction occurs, be it online or offline, encryption algorithms are used to transform the card details into a secure format.
This process, known as data encryption, makes it extremely difficult for unauthorized individuals to access or decipher the card information.
Encryption is particularly important in online transactions, where data is transmitted over public networks and is more susceptible to interception and misuse.
The SSL (Secure Socket Layer) and TLS (Transport Layer Security) protocols are fundamental to encrypting data in online transactions. These protocols create a secure connection between the customer’s browser and the merchant’s server, safeguarding the data exchange process.
When a user enters their credit card information on a website, SSL/TLS encrypts this information before it travels over the internet, ensuring it remains confidential and secure until it reaches its intended destination.
This encryption mechanism protects the data from being intercepted and helps build trust with customers, assuring them that their financial transactions are secure.
Mobile wallets like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay use advanced technologies to make paying for things easy and secure.
They turn your phone into a digital wallet, so you don’t need to carry physical cards or cash.
These mobile wallets use a technology called Near Field Communication (NFC) which lets your phone communicate with the payment terminal.
When you hold your phone close to the terminal, NFC sends your payment info securely without you having to touch anything. This is why it’s called “contactless” payment – you just tap your phone and go.
Another cool tech in mobile payments is QR codes. You’ve probably seen these square, barcode-like images. Some mobile wallets use them for payments.
You just scan the QR code with your phone’s camera, and it processes your payment. It’s handy when you want to pay without touching anything or when NFC isn’t available.
QR codes are also great for small businesses because they’re easy to set up and use.
Payment gateway technologies have seen remarkable advancements, making online transactions faster, safer, and more convenient. One of the key features of modern payment gateways is real-time transaction processing.
This means that when you buy something online, the payment gets processed almost instantly, letting both you and the seller quickly know that the transaction was successful. This speed and efficiency are crucial for a good online shopping experience.
Another important aspect of these technologies is advanced fraud detection. Payment gateways now use sophisticated tools to spot suspicious activities, helping to prevent unauthorized or fraudulent transactions.
This adds a layer of security, protecting both businesses and customers. Additionally, these gateways are designed for seamless integration.
They easily fit into various e-commerce platforms and systems, ensuring businesses can set them up without much hassle and customers can use them easily across different online stores.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) plays a pivotal role in enhancing the capabilities of fraud detection systems. By analyzing vast amounts of transaction data,
AI can identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activity. Machine learning algorithms, a core component of AI, are particularly effective in this regard. They continuously learn from new data, adapting and improving their ability to spot potential fraud.
This means they better distinguish between legitimate and suspicious activities as they process more transactions.
The dynamic and self-improving nature of machine learning algorithms significantly boosts the accuracy and efficiency of fraud prevention systems, making them indispensable tools in the ongoing battle against financial fraud.
Real-time transaction processing technology is essential in the fast-paced consumer environment. It ensures that credit card transactions are processed instantly, meeting the modern consumer’s expectation for speed and efficiency.
This quick processing is crucial in various scenarios, such as online shopping or dining, where delays can negatively affect the customer experience.
The ability to process transactions without delay satisfies customers and streamlines business operations.
The significance of providing a seamless and quick payment experience cannot be understated. It aligns with the increasing preference for digital and mobile payments, catering to a tech-savvy consumer base.
This integration of instant processing technology in payment systems is vital in enhancing customer satisfaction and maintaining business efficiency in a digitally driven market.
Cross-border payment technologies are evolving to address the unique challenges posed by international credit card transactions. These challenges include currency exchange, differing payment regulations across countries, and varying transaction fees.
Advanced technologies in this domain are geared towards simplifying these processes, ensuring efficient and cost-effective transactions regardless of geographical boundaries.
Innovations in real-time currency conversion are critical to these technologies, enabling consumers and merchants to seamlessly transact in different currencies without facing the hurdles of high conversion fees and exchange rate uncertainties.
Furthermore, these technologies aim to reduce the complexities of cross-border transactions. This includes improving the speed of transactions, ensuring compliance with international payment standards, and enhancing security measures to protect against fraud in a global context.
By streamlining these processes, cross-border payment technologies facilitate smoother international commerce and open new business markets, fostering global economic connectivity.
Integrating these technologies into payment systems represents a significant step towards a more interconnected and efficient global financial ecosystem.
The ongoing evolution in credit card processing and payment technologies reflects a larger trend toward creating a more secure, efficient, and user-friendly financial ecosystem.
From the advent of real-time transaction processing that caters to the modern consumer’s need for speed to the sophisticated AI-driven fraud detection systems that safeguard transactions, each innovation marks a significant step forward in financial technology.
Moreover, advancements in cross-border payment technologies are dismantling the traditional barriers of international commerce, paving the way for a more interconnected global economy.
Collectively, these developments are enhancing the payment experience for consumers and merchants alike and shaping the future of how we manage and execute financial transactions in an increasingly digital world.
Interchange fees are fees paid between banks to accept card-based transactions. Typically, these fees are paid by the merchant’s bank (acquiring bank) to the cardholder’s bank (issuing bank) and are associated with the costs of processing transactions, fraud, bad debt risks, and the benefits of accepting card payments.
The rules for contactless payments vary by region and card issuer, but generally, they involve limits on the transaction amount for a single contactless payment to enhance security. In some regions, contactless transactions may require a PIN or signature for amounts above a certain threshold, and there are often cumulative limits after which a PIN is required.
A cash advance payment is typically when you use your credit card to withdraw cash from an ATM. This type of transaction often incurs additional fees and higher interest rates than regular credit card purchases, and interest starts accruing immediately without a grace period.
